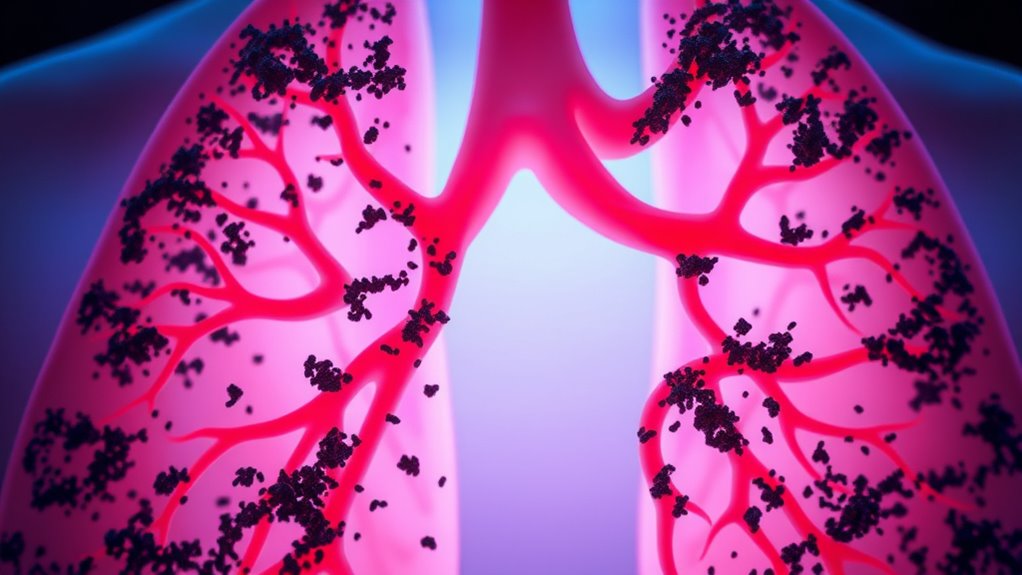
When you breathe, tiny particulate matter can bypass your body’s natural defenses and deposit deep in your respiratory system, especially if the particles are smaller than 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5). Larger particles tend to settle in your nose and throat, while ultrafine particles can reach your alveoli, where oxygen exchange happens. Over time, these particles can cause inflammation, worsen respiratory conditions, and even enter your bloodstream. To better understand how this impacts your health, keep exploring further.
Key Takeaways
- Larger particles (dust, pollen) deposit mainly in the nose and throat through mucous trapping.
- Fine particles (<2.5 micrometers, PM2.5) penetrate deep into the lungs, reaching alveoli.
- Particles can embed in alveoli or enter the bloodstream, affecting systemic health.
- The respiratory system’s natural defenses may become overwhelmed with prolonged or high exposure.
- Proper air filtration, like HEPA filters, reduces inhalation of deposited particulate matter.
Have you ever wondered how tiny particles in the air can affect your lungs? These microscopic specks, known as particulate matter, are small enough to bypass your body’s natural defenses and settle deep into your respiratory system. The health effects of inhaling these particles can range from mild irritation to serious respiratory diseases. When particles lodge in your lungs, they can trigger inflammation, worsen asthma, or even contribute to chronic conditions like bronchitis and COPD. That’s why understanding how particulate matter deposits in your respiratory system is essential for protecting your health. Recognizing the importance of air purification can significantly reduce your exposure to harmful particles.
Air purification becomes an indispensable part of reducing your exposure to these harmful particles. Air purifiers with HEPA filters are designed to trap a significant portion of particulate matter before it reaches your lungs. By removing these particles from indoor air, you can reduce the risk of adverse health effects and improve overall air quality. Keep in mind, though, that not all air purifiers are equally effective; selecting one with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter is your best bet for capturing fine particles, including those that are even smaller than the width of a human hair.
Using HEPA filters in air purifiers significantly reduces indoor particulate matter and protects your respiratory health.
When you breathe in, particles follow different paths depending on their size. Larger particles, such as dust or pollen, tend to deposit in your nose and throat, where your body’s mucous membranes catch and expel them. Smaller particles, especially those less than 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5), can penetrate deeper into your lungs, reaching the alveoli—the tiny air sacs where oxygen exchange occurs. Once there, some particles may stay embedded, while others can even enter your bloodstream, causing systemic health effects.
Your body’s natural defense mechanisms try to clear these particles, but their effectiveness diminishes with prolonged exposure or high concentrations. Persistent inhalation of fine particulate matter can overwhelm your lungs’ ability to clear debris, leading to inflammation and structural damage over time. This is why reducing indoor particulate levels through air purification is essential, especially if you live in areas with high pollution or have existing respiratory issues.
Incorporating air purification strategies into your daily routine can make a tangible difference. Regularly changing filters, ventilating your space, and avoiding sources of indoor pollution—like smoking or burning candles—are simple but effective steps. Being aware of how particulate matter deposits in your respiratory system empowers you to take action, protecting your lungs and supporting your overall health. After all, cleaner air means a healthier, more comfortable life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Particle Size Influence Respiratory Health Effects?
Smaller particles, like PM2.5, penetrate deeper into your lungs due to aerosol penetration, increasing health risks. Larger particles tend to agglomerate and deposit in your upper respiratory tract, causing irritation. As particle size decreases, the likelihood of reaching delicate lung tissues rises, heightening the chance of respiratory issues. So, particle size directly influences how deeply particles deposit, affecting your respiratory health outcomes.
What Are the Long-Term Consequences of Particulate Matter Accumulation?
Did you know that long-term particulate matter exposure can increase respiratory disease risk by 30%? Over time, particles build up in your lungs, causing chronic inflammation and taxing your immune response. This buildup can lead to reduced lung function, chronic bronchitis, or even cardiovascular issues. If you don’t reduce exposure, these long-term consequences may considerably diminish your quality of life and overall health.
Can Natural Remedies Reduce Particulate Matter Deposition?
Natural remedies like herbal detox and dietary antioxidants may help support your respiratory health, but they won’t directly reduce particulate matter deposition. These remedies can strengthen your immune system and reduce inflammation, making you better equipped to handle pollutants. However, the best way to minimize PM deposition is to avoid exposure. Incorporate antioxidants and herbal detox into your routine alongside protective measures like wearing masks and avoiding polluted areas.
How Do Different Pollutants Interact Within the Respiratory System?
Different pollutants interact within your respiratory system through chemical interactions that can intensify their harmful effects. For example, gases like ozone can react with particulate matter, creating more reactive compounds. These interactions can trigger your immune response, leading to inflammation and irritation. Understanding these processes helps you recognize how combined pollutants exacerbate respiratory issues and underscores the importance of reducing exposure to protect your lungs.
What Are Emerging Technologies for Monitoring Particulate Matter Exposure?
Ever wonder how you can stay ahead of pollution? Emerging technologies like advanced air quality sensors and wearable monitors now let you track particulate matter exposure in real time. These devices provide immediate data on pollution levels, empowering you to take action and reduce health risks. With continuous improvements, you can better understand your environment and make smarter decisions to protect your respiratory health every day.
Conclusion
As you breathe, tiny particles gently settle within your respiratory system, quietly influencing your health. While these particles are often just a subtle part of your environment, being mindful helps you enjoy cleaner air and better well-being. Embrace simple habits like staying indoors during heavy pollution or wearing masks when needed. By doing so, you create a gentle shield around your lungs, allowing you to breathe easier and savor life’s moments with a lighter, more comfortable breath.