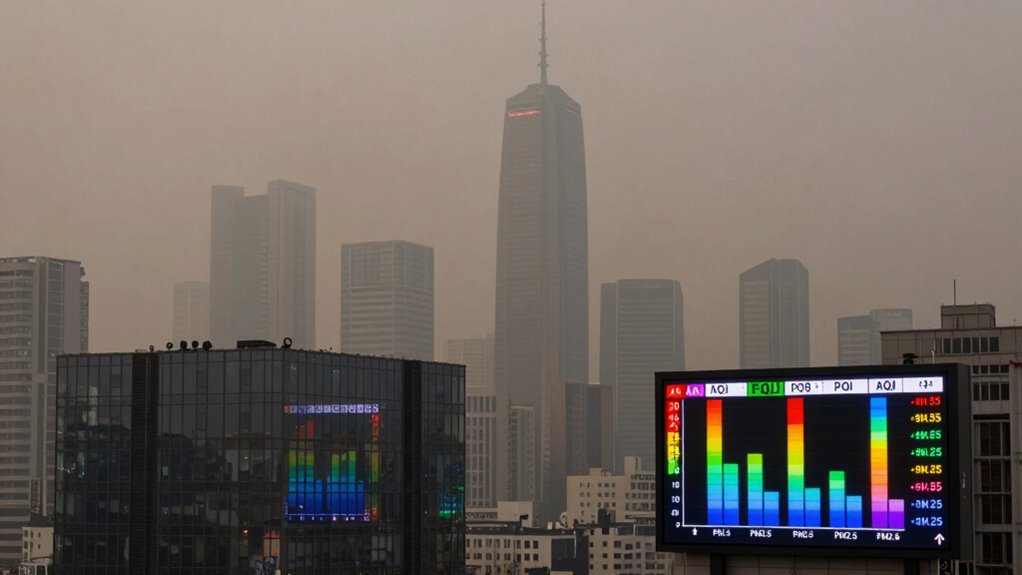
Understanding the difference between AQI and PM2.5 is key to evaluating air quality accurately. AQI gives a single number summarizing multiple pollutants, making it easy to gauge overall air health. PM2.5 measures tiny particles that can harm your lungs specifically. Confusing these can lead to misjudging safety; knowing how they work helps you interpret air conditions better. Keep exploring to discover how proper measurements protect your health and guide smarter choices.
Key Takeaways
- AQI combines multiple pollutants into a single score, while PM2.5 measures only tiny particulate matter.
- AQI provides an overall air quality snapshot; PM2.5 offers detailed info on specific harmful particles.
- Differences in calculation and standards can lead to confusion when interpreting air quality data.
- Proper calibration and measurement accuracy are essential for reliable AQI and PM2.5 readings.
- Understanding both metrics helps make better health decisions and avoid misinterpreting air pollution levels.

Air quality measurement often involves two key indicators: the Air Quality Index (AQI) and PM2.5 levels. While they’re related, understanding how each works and their differences can be confusing. The AQI provides a simple, numerical scale that summarizes overall air pollution, making it easier for the general public to interpret air quality conditions at a glance. It aggregates various pollutants into a single number, which helps you quickly assess whether the air is safe, moderate, or hazardous. On the other hand, PM2.5 levels focus specifically on tiny particulate matter measuring 2.5 micrometers or smaller. These particles are especially harmful because they can penetrate deep into your lungs and even enter your bloodstream.
Understanding the differences between AQI and PM2.5 helps you interpret air quality more accurately.
One key aspect that influences both measurements is adherence to air quality standards. These standards are set by agencies like the EPA, which determine what levels of pollutants are considered safe based on current scientific knowledge. They serve as benchmarks to guide measurement accuracy and protect public health. When monitoring air quality, guaranteeing measurement accuracy is indispensable; inaccurate readings can either cause unwarranted alarm or give a false sense of safety. For example, if PM2.5 sensors aren’t calibrated properly, they might underreport pollution levels, leading you to believe the air is cleaner than it actually is. Similarly, if the AQI calculation doesn’t account for local pollution sources or fluctuates due to measurement errors, it can misrepresent the true air quality situation. Ensuring measurement accuracy and calibration is essential for reliable air quality assessments.
The challenge arises because the AQI is a composite index that considers multiple pollutants, including ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and PM2.5. Its calculation involves complex algorithms that translate pollutant concentrations into a single, easy-to-understand number. This simplification, while user-friendly, can sometimes obscure the specific contributions of PM2.5 to overall air pollution. Conversely, focusing solely on PM2.5 levels provides detailed insights into a particularly dangerous component but doesn’t give the full picture of air quality.
Because of these differences, understanding both the AQI and PM2.5 measurements is fundamental for making informed decisions about outdoor activities and health precautions. Proper measurement accuracy and adherence to air quality standards ensure that these indicators reflect reality, protecting you from health risks associated with air pollution. In essence, recognizing what each metric tells you helps cut through the confusion and empowers you to respond appropriately to changing air quality conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Weather Affect AQI and PM2.5 Levels?
Weather impact plays a big role in air quality variability, affecting both AQI and PM2.5 levels. When the weather is calm, pollution tends to accumulate, raising these levels. Wind can disperse pollutants, improving air quality, while rain helps clear particles from the air. Temperature inversions trap pollutants close to the ground, worsening air quality. So, you’ll notice pollution levels fluctuate with changing weather patterns, directly influencing your air quality.
Are Healthy Individuals Unaffected by High PM2.5 Concentrations?
Even healthy individuals can be affected by high PM2.5 levels—studies show that long-term exposure increases cardiovascular and respiratory risks. While air quality standards aim to protect everyone, you might not notice immediate effects, but your personal health can still suffer over time. It’s smart to stay informed about pollution levels and limit outdoor activities during high PM2.5 days to safeguard your well-being.
Can AQI and PM2.5 Readings Be Inaccurate?
Yes, AQI and PM2.5 readings can be inaccurate if sensors aren’t properly calibrated or if data reporting isn’t maintained correctly. You should check the calibration status of your sensors regularly, as miscalibrated devices can give false readings. Inaccurate data reporting can also skew the perceived air quality, leading to misunderstandings about health risks. Staying vigilant with calibration and data accuracy helps make sure reliable air quality information for you.
Which Pollutants Are Included in AQI Calculations?
You should know that AQI calculations include pollutants like ground-level ozone, PM2.5, PM10, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. These pollutants come from various sources such as vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and natural events. Regional differences matter, as pollutant sources and levels vary across areas, affecting AQI readings. This means your local AQI reflects specific regional pollution, helping you understand air quality risks better.
How Often Are AQI and PM2.5 Monitored?
Imagine your air quality as a heartbeat—constant and essential. You usually get updates daily or hourly, thanks to advanced monitoring technology that tracks pollutants like PM2.5. Agencies follow strict air quality standards to guarantee accuracy. These updates help you understand pollution levels, so you can take action if needed. Regular monitoring keeps you informed about your environment, making sure you breathe easier and stay safe every single day.
Conclusion
So, next time you see AQI and PM2.5 numbers, picture them as two maps guiding you through a foggy landscape. AQI is the overall trail marker, showing the big picture of air quality, while PM2.5 is like zooming in on tiny, dangerous spots. Don’t get lost in the confusion—understanding their roles helps you navigate the air quality maze with confidence. After all, clarity is your compass in the fog.